Installation¶
Software Requirements¶
It is recommended to run Field-TM on a Linux-based machine.
This includes MacOS, but some tools must be substituted.
For Windows users, the easiest option is to use Windows Subsystem for Linux
Before you can install and use this application, you will need to have the following software installed and configured on your system:
If running Debian/Ubuntu, the install script below does this for you.
Git to clone the Field-TM repository.
Docker to run Field-TM inside containers.
Docker Compose for easy orchestration of the Field-TM services.
This is Docker Compose V2, the official Docker CLI plugin.
i.e.
docker composecommands, notdocker-compose(the old tool).
Easy Install¶
On a Linux-based machine with bash installed, run the script:
Note: it is best to run this script as a user other than root.
However, if you run as root, a user svcfmtm will be created for you.
curl -L https://get.fmtm.dev -o install.sh
bash install.sh
# Then follow the prompts
Manual Install¶
If more details are required, check out the dev docs
Table of Contents¶
- Installation
Clone the Field-TM repository¶
Clone the repository to your local machine using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/hotosm/field-tm.git
# If you wish to deploy for production, change to the main branch
git checkout main
Setup Your Local Environment¶
These steps are essential to run and test your code!
1. Setup OSM OAuth 2.0¶
The Field-TM uses OAuth with OSM to authenticate users.
To properly configure your Field-TM project, you will need to create keys for OSM.
-
Login to OSM (If you do not have an account yet, click the signup button at the top navigation bar to create one).
Click the drop down arrow on the top right of the navigation bar and select My Settings.
-
Register your Field-TM instance to OAuth 2 applications.
Put your login redirect url as
http://127.0.0.1:7051/osmauthif running locally, or for production replace with https://{YOUR_DOMAIN}/osmauthNote:
127.0.0.1is required for debugging instead oflocalhostdue to OSM restrictions.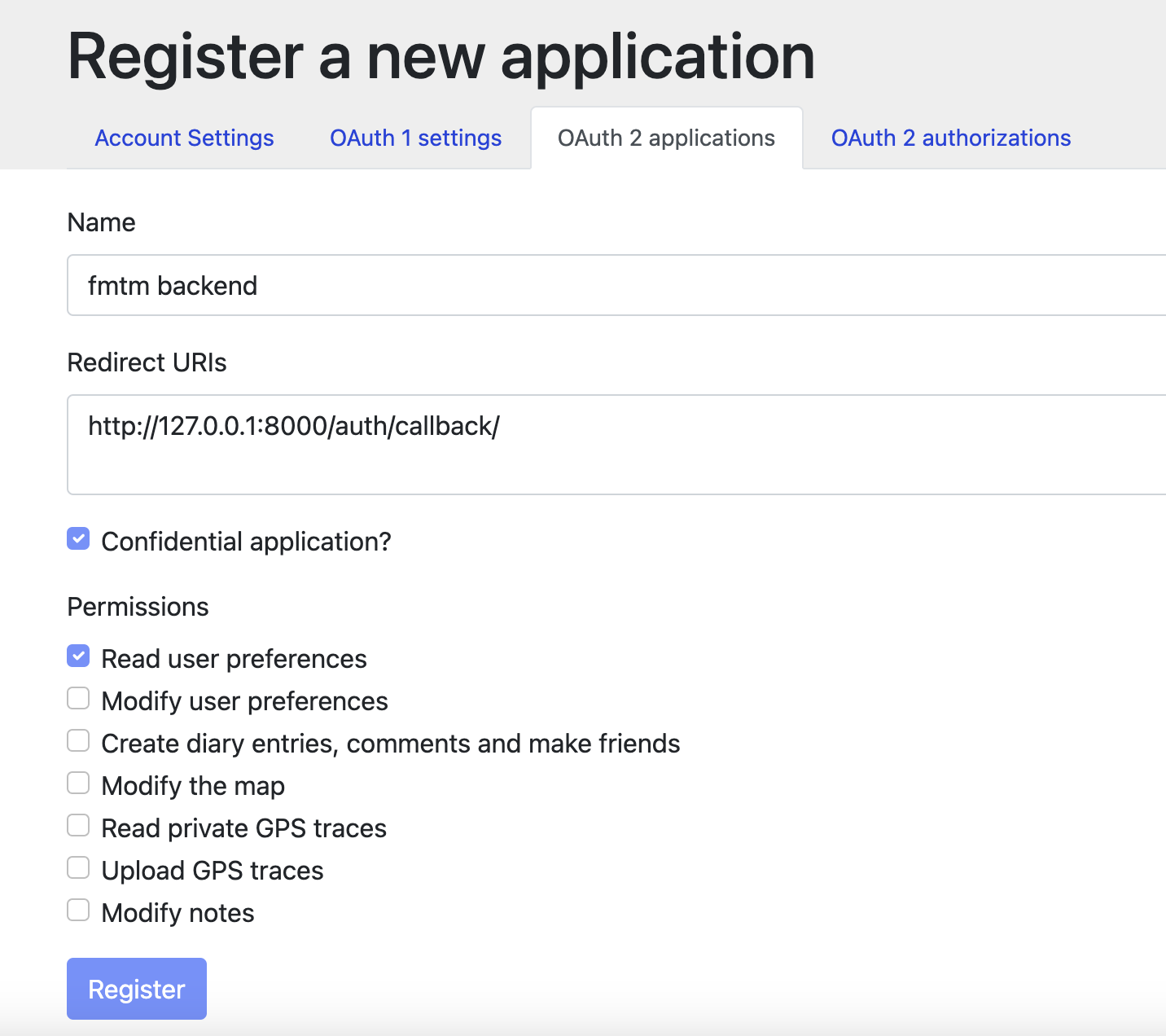
-
Add required permissions:
- 'Read user preferences' (
read_prefs) - 'Send private messages to other users' (
send_messages)
- 'Read user preferences' (
-
Now save your Client ID and Client Secret for the next step.
2. Create an .env File¶
Environmental variables are used throughout this project.
To get started, create .env file in the top level dir,
a sample is located at .env.example.
This can be created interactively by running:
bash scripts/1-environment/gen-env.sh
Note: If extra cors origins are required for testing, the variable
EXTRA_CORS_ORIGINSis a set of comma separated strings, e.g.: http://fmtm.localhost:7050,http://some.other.domainNote: It is possible to generate the auth pub/priv key manually using: openssl genrsa -out field-tm-private.pem 4096 openssl rsa -in field-tm-private.pem -pubout -out field-tm-private.pem
Start the API with Docker¶
This is the easiest way to get started with Field-TM.
Docker runs each service inside containers, fully isolated from your host operating system.
Select the install type¶
Determine the what type of Field-TM install you would like:
main - the latest production
staging - the latest staging
dev - the latest development (warning: may be unstable)
local dev - used during development, or to start a test version
The corresponding docker-compose files are:
main - deploy/compose.main.yaml
staging - deploy/compose.staging.yaml
dev - deploy/compose.dev.yaml
local test - compose.yaml
Set your selection to a terminal variable to make the next step easier:
export COMPOSE_FILE={your_selection}
# E.g.
export COMPOSE_FILE=deploy/compose.dev.yaml
Pull the Images¶
docker compose -f "${COMPOSE_FILE}" pull
This will pull the latest containers for the branch you selected.
Build the Frontend¶
Before we can run, you need to build your version of the frontend.
This is because the frontend contains variable specific to your deployment.
docker compose -f "${COMPOSE_FILE}" build ui
Start the Containers¶
docker compose -f "${COMPOSE_FILE}" up -d
You should see the containers start up in order.
Once complete, you should now be able to navigate to the project in your browser:
https://{YOUR_DOMAIN}
# For the local test setup, this will be
http://fmtm.localhost:7050
Note: If those link doesn't work, check the logs with
docker compose logs api.Note: Use
docker psto view all container names.
Setup ODK Central User (Optional)¶
The Field-TM uses ODK Central to store ODK data.
- By default, the docker setup includes a Central server.
- The credentials should have been provided in your
.envfile to automatically create a user. - To create a user manually:
docker compose exec central odk-cmd --email YOUREMAIL@ADDRESSHERE.com user-create
docker-compose exec central odk-cmd --email YOUREMAIL@ADDRESSHERE.com user-promote
Note: Alternatively, you may use an external Central server and user.
Set Up Monitoring (Optional)¶
- There is an optional configuration for application monitoring via OpenTelemetry.
-
To enable this set in your
.envfile:# For OpenObserve MONITORING="openobserve" # For Sentry MONITORING="sentry"
- Check the
.env.examplefor additional required parameters. - Everything should be configured for you to see endpoint calls in the selected web dashboard, providing full error tracebacks and stats.
Check Authentication (Optional)¶
Once you have deployed, you will need to check that you can properly authenticate.
-
Navigate to your frontend (e.g.
http://fmtm.localhost:7050) -
Click the 'Sign In' button and follow the popup prompts.
-
If successful, you should see your username in the header.
-
If you see an error instead, double check your credentials and redirect URL in the openstreetmap.org settings.
Frontend Customization (Optional)¶
- It's possible to tailor the mapper portion of Field-TM to your needs (the main app that users will see).
-
There is a
config.jsonfile that is used to dynamically modify the frontend deployment:{ "logoUrl": "/favicon.svg", "logoText": "Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team", "cssFile": "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@hotosm/ui@0.2.0-b6/dist/style.css", "enableWebforms": false, "loginProviders": { "osm": true, "google": true }, "sidebarItemsOverride": [] }
- This is read from the bundled Minio S3 bucket called
fmtm-data:https://s3.{YOUR_FIELDTM_DOMAIN}/fmtm-data/frontend/config.json - Under the
fmtm-data/frontendpath you can modify theconfig.json, and also upload things like CSS files and logos.
Configure Custom Branding¶
- It's possible to replace the HOTOSM logo and change the colour scheme for your deployment.
-
This file will be automatically picked up and used to style your application. By default, Field-TM will fallback to the bundled
config.json.{ ... "logoUrl": "/favicon.svg", "logoText": "Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team", "cssFile": "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@hotosm/ui@0.2.0-b6/dist/style.css" }
Configure Custom Favicon¶
- During deploy, place your
favicon.svgin the root of the repo. - Run the deployment script, and the favicon + generated PNG version will be used in your frontend deployment automatically.
Configure Custom Sidebar Elements¶
- By default Field-TM has a few items in the sidebar, like a link to a support page, and other resources.
-
These links can be overridden using the
sidebarItemsOverrideparameter in theconfig.json, which expects format:{ ... "sidebarItemsOverride": [ { "name": "Your Website", "path": "https://yourwebsite.com" }, { "name": "Support", "path": "https://docs.fmtm.dev/about/about/" } ] }
Enabled / Disable Auth Providers¶
-
We are continually adding new OAuth provider options.
{ ... "loginProviders": { "osm": true, "google": true } }
That's it, you have successfully set up Field-TM!!